Professional manufacturer with the design, development and production of rubber and plastic machinery
Exploring the Technical Aspects of Internal Rubber Kneaders: A Comprehensive Guide
Sep 11,2025
Exploring the Technical Aspects of Internal Rubber Kneaders
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Internal Rubber Kneaders
- What is an Internal Rubber Kneader?
- Mechanics of Internal Kneaders
- Applications of Internal Rubber Kneaders
- Advantages of Using Internal Rubber Kneaders
- Challenges and Limitations
- Maintenance and Optimization of Internal Rubber Kneaders
- Future Trends in Rubber Processing
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Introduction to Internal Rubber Kneaders
Internal rubber kneaders have become an integral part of the rubber processing industry. Their efficiency and effectiveness in mixing and kneading rubber compounds have made them a preferred choice for manufacturers. In this article, we will explore the technical aspects of internal rubber kneaders, detailing their mechanics, applications, advantages, and more.
What is an Internal Rubber Kneader?
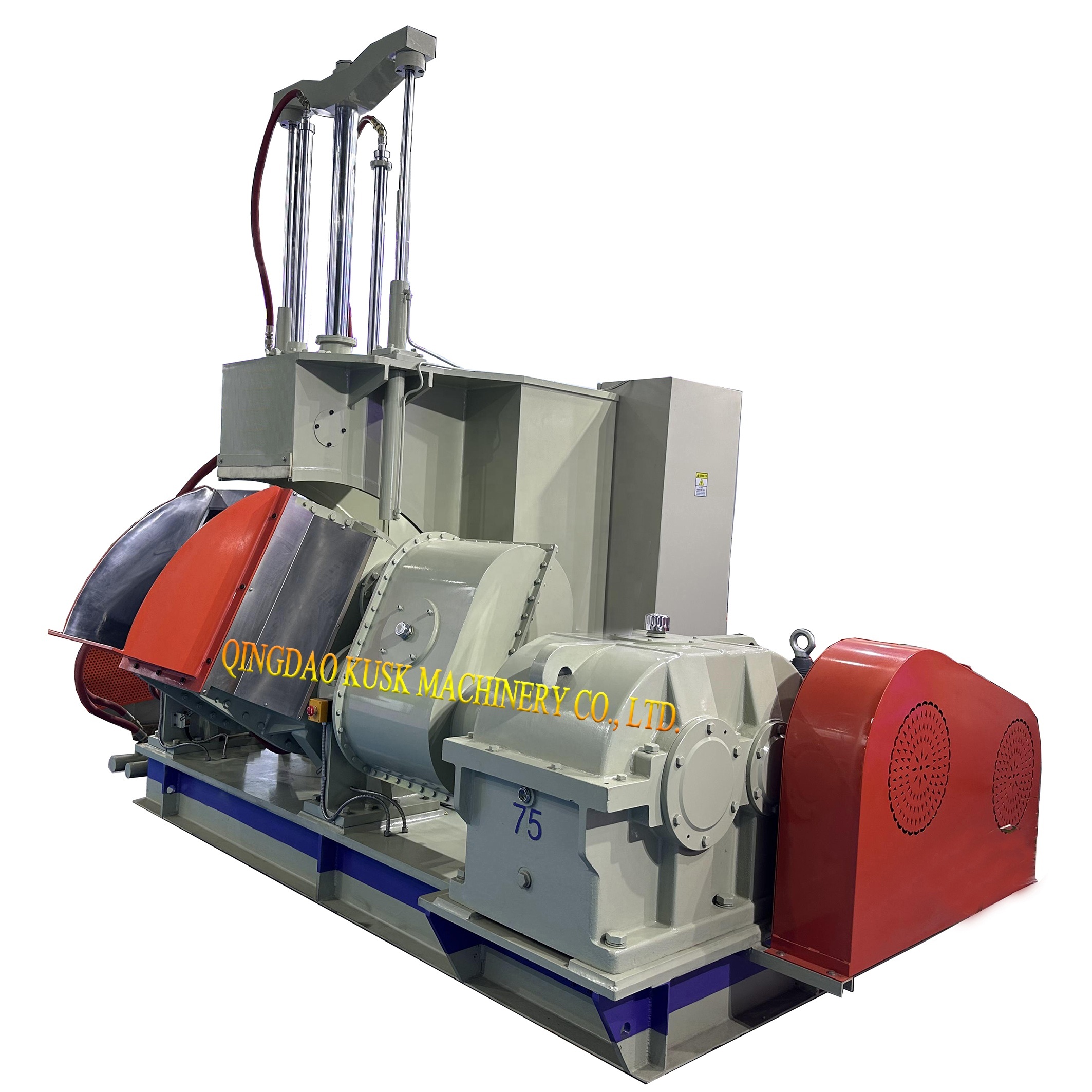
An **internal rubber kneader** is a type of mixer specifically designed for the preparation of rubber compounds. It typically consists of a chamber where the rubber materials are processed using rotors that knead the materials together. The design allows for effective mixing while controlling the temperature and viscosity of the compounds, resulting in a well-blended product.
How Do Internal Rubber Kneaders Work?
The operation of internal rubber kneaders involves two main rotors that rotate in opposite directions. As the rotors turn, they create a shearing action that thoroughly mixes the rubber with additives like carbon black, oils, and other polymers. This process is critical for achieving uniformity in the final product.
Mechanics of Internal Kneaders
Understanding the mechanics of internal rubber kneaders is essential for optimizing their performance. The design and structure, as well as the mixing principles involved, play a significant role in their efficiency.
Design and Structure
The design of internal rubber kneaders typically features a **U-shaped chamber** where the mixing occurs. This design allows for a more effective mixing process. Additionally, the rotors are generally made from high-strength materials to withstand the high stresses involved in the mixing process.
Rotor Types and Configurations
Different rotor types can be employed in internal rubber kneaders, including **sigma blades**, **intermeshing rotors**, and **counter-rotating rotors**. Each type has its advantages, depending on the specific application and desired outcome.
Mixing Principles
The mixing principles in internal rubber kneaders revolve around three key factors: **shear**, **temperature**, and **viscosity**. Understanding how these elements interact can allow operators to fine-tune the kneading process for optimal results.
Applications of Internal Rubber Kneaders
Internal rubber kneaders find applications across various sectors, primarily in the rubber and plastics industry. They are commonly used for:
- Producing rubber compounds for tires
- Manufacturing rubber seals and gaskets
- Creating rubber sheets for various applications
- Mixing elastomers with additives to achieve desired properties
Advantages of Using Internal Rubber Kneaders
There are numerous **advantages** to utilizing internal rubber kneaders in rubber processing. These include:
- **High Efficiency**: Internal kneaders provide a thorough mixing process, reducing batch times.
- **Temperature Control**: The design allows for effective temperature management, helping to prevent overheating of the rubber.
- **Flexibility**: Adjustments can be made to the rotor speed and chamber temperature to accommodate different materials and desired outcomes.
- **Consistency**: The mixing action ensures a uniform distribution of materials, resulting in a consistent final product.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, internal rubber kneaders also face several **challenges** and **limitations**:
- **Wear and Tear**: The rotors and chamber walls can suffer wear over time, which may affect performance.
- **Energy Consumption**: Internal kneaders can be energy-intensive, leading to higher operational costs.
- **Material Limitations**: Certain types of rubber compounds may not mix well in an internal kneader, requiring alternative processing methods.
Maintenance and Optimization of Internal Rubber Kneaders
To ensure optimal performance of internal rubber kneaders, regular maintenance is essential. Key maintenance practices include:
- **Routine Inspections**: Regular checks of the rotors, chamber, and seals for wear and damage.
- **Lubrication**: Keeping mechanical parts properly lubricated to minimize friction and wear.
- **Calibration**: Periodic calibration of temperature and speed settings to ensure they meet production specifications.
Future Trends in Rubber Processing
The rubber processing industry is evolving, and several trends indicate the future direction of internal rubber kneaders:
- **Automation and Smart Technology**: Increasing integration of AI and automation technologies to enhance the efficiency and precision of the kneading process.
- **Sustainability**: A push towards developing eco-friendly materials and processes, including the use of renewable resources in rubber production.
- **Advanced Materials**: The development of new rubber formulations that require specialized processing techniques may lead to innovations in kneader design.
Conclusion
Internal rubber kneaders are indispensable tools in the rubber processing industry, offering high efficiency, flexibility, and the ability to produce a consistent product. By understanding the technical aspects of these machines—from their mechanics to their applications and advantages—we can better appreciate their role in modern manufacturing. As the rubber industry continues to evolve, internal rubber kneaders will likely adapt, incorporating new technologies and materials that will further enhance their effectiveness.
FAQs
1. What is the primary function of an internal rubber kneader?
The primary function of an internal rubber kneader is to mix rubber compounds efficiently, ensuring a uniform blend of materials.
2. How do I maintain an internal rubber kneader?
Regular inspections, lubrication of mechanical parts, and calibration of operational settings are essential for maintaining an internal rubber kneader.
3. What are the typical applications of internal rubber kneaders?
They are commonly used in tire production, rubber seals, gaskets, and mixing various elastomers.
4. What challenges do internal rubber kneaders face?
Challenges include wear and tear on components, high energy consumption, and the limitations of mixing certain rubber compounds.
5. How can I optimize the performance of my internal rubber kneader?
Optimizing performance can be achieved through regular maintenance, appropriate settings adjustments, and ensuring the right materials are used for specific applications.
Hot Tags:
Contact Us
E-mail:
tender701@gmail.com
tender701@163.com
Phone/WhatsApp:
+86 137 9243 6835
Address:
Huangshan Economic Zone, Huangdao, Qingdao,China